How do nitrogen generators assist with precision laser cutting
How do nitrogen generators assist with precision laser cutting
Laser cutting is a process that uses high power, precision laser beam to cut metals such as stainless steel and aluminum for industrial and commercial use.Usually, auxiliary gas is used to help lasers provide clean cutting and optimal performance.The choice of which gas to use depends on certain factors, such as the type of material being cut, the required cut quality, and the thickness of the material.
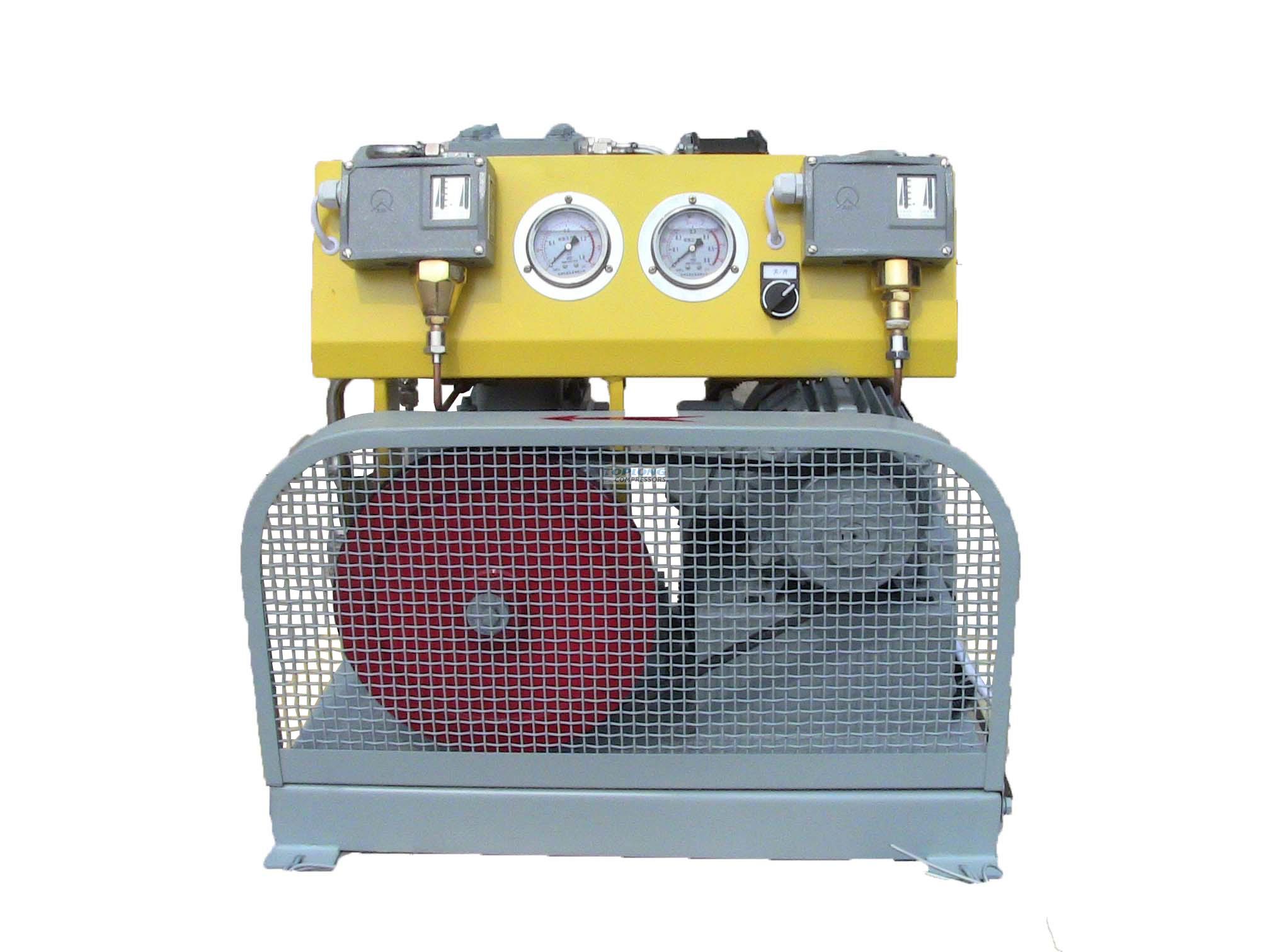
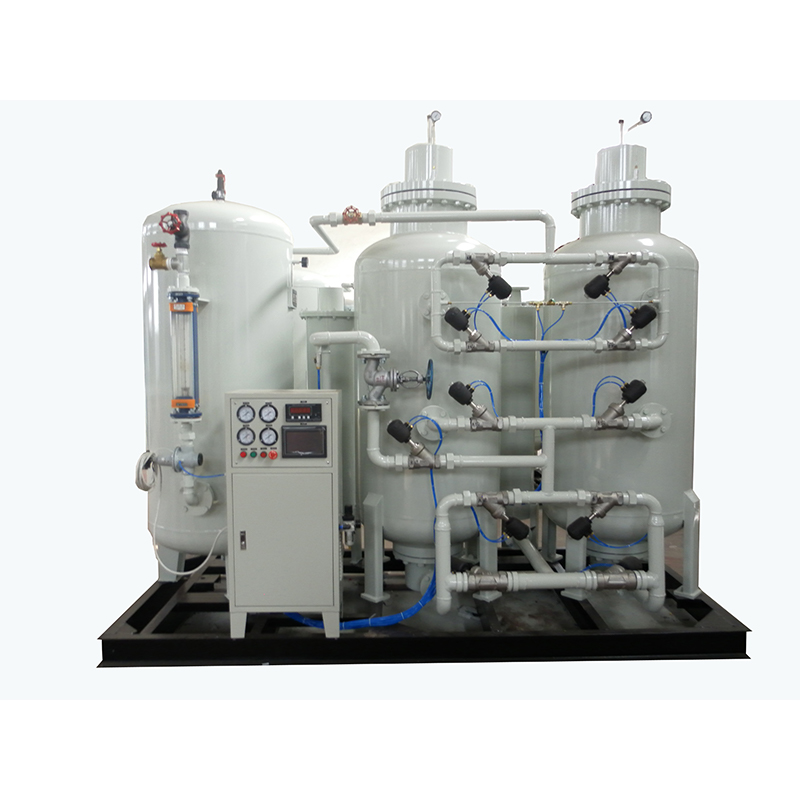
Today, the most common type of laser-cutting auxiliary gas is nitrogen.It is the most commonly used gas because of its multiple advantages during laser-cutting processes.For example, a nitrogen-assisted laser can cut the metal without burning or discolored the material, different from when other gases such as oxygen are used to assist.In addition, nitrogen has the unique ability to evaporate the metal from the cutting edge before it has a chance to reset, thus providing you with cleaner cuts and thus improving the quality of the final product.
Laser cutting for nitrogen gas application
While the initial cost of nitrogen laser cutting may be slightly higher than oxygen laser cutting, the use of nitrogen as an auxiliary gas can provide products without any additional finishing and can save you money in the long run.Here are some examples of laser-cutting nitrogen applications::
Low carbon steel and stainless steel: For low carbon steel and stainless steel applications, maximum oxidation is usually required.Although oxygen-driven laser cutting has a limited cutting speed, its corresponding nitrogen can produce higher power, enabling faster cutting.Therefore, nitrogen is well suited to this particular application because it can be cut faster and more precisely than any other alternative.
Plasma Cutting Steel: If you're looking for clean cutting and weldable edges, plasma cutting is your best choice.When using nitrogen as an auxiliary gas in this application, it enables rapid, clean cutting without further processing.Instead, using oxygen as an auxiliary gas introduces contaminants, resulting in oxidation that is difficult to clean.
Plasma-cut aluminum: Compressed air may be the most affordable option, but using oxygen is not the best choice for this application.Therefore, nitrogen is the best choice in terms of cost, quality, and cutting speed when handling thinner metal applications such as aluminum.